Newag E6 ‘Dragon’ family / ET25 /
ET26 / ET43
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
My first encounter with the E6ACT prototype yielded a few photos –
this is the best one… Zduńska Wola Karsznice, September
9, 2011. Take
two was more successful; TRAKO 2011 Fair in Gdańsk,
October 14, 2011. Cab
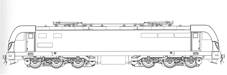
interior, photographed on the same occasion. Side drawing published in a ZNLE
folder. E6ACT-005 operated by Lotos Kolej,
photographed in Zduńska Wola
Karsznice on April 21, 2014. E6ACT-002 operated by STK,
photographed near the Warszawa Wawer station on
October 17, 2015. E6ACT-008, Lotos Kolej,
photographed at the TRAKO 2015
fair in Gdańsk, September 22, 2015. Photo by Chris
West (thanks for permission!). E6ACT-006, Lotos Kolej,
photographed in Zduńska Wola
Karsznice on May 21, 2016. E6ACTd-106 is operated by Budokrusz building materials company; photographed
near Warszawa Praga station on October 12, 2017,
still in the manufacturer’s livery. Another photo of the E6ACT-006: Puławy
Azoty station, October 3, 2018. E6ACTa-002 on display at the InnoTrans fair in Berlin, September 20, 2018; photo by Chris
West (used by permission). E6ACTadb-035, operated by Laude
Smart Intermodal, photographed near Jakubowice
on September 13, 2020. The same locomotive photographed in Morąg on October 10, 2020. E6ACTadb-035 once again: Pilawa,
July 4, 2024. E6ACTa-007 is owned by Newag; leased to CTL Logistics in January 2019 and to Rail STM two years later. Photo taken in Piwniczna
on March 4, 2021. E6ACTab-037 from the Lotos Kolej
fleet, sporting an untypical livery. Puławy Azoty station, January 30, 2022. The same location, June 12, 2022: ET26-002 from the
PKP Cargo fleet. E6ACTad-026, operated by ZPK
Szumowo, photographed near
Warszawa Żerań station on August 10, 2023. ET26-004, PKP Cargo, Warszawa
Praga station, April18, 2024. ET26-007, PKP Cargo,
the same location, June 27, 2024. Warszawa Praga again:
ET26-005, PKP Cargo, August 22, 2024. ET26-003, PKP Cargo,
photographed at the Puławy Azoty
station exactly one month later. E6ACT-006, Lotos Kolej,
photographed at the Warszawa Praga station on
November 7, 2024; in 2024 Lotos Kolej and Orlen
KolTrans merged to form Orlen Kolej. The same location: ET26-001… … and ET26-003, PKP
Cargo, April 3, 2025. |
After
main Polish locomotive manufacturers either had been taken over by foreign
companies or had withdrawn from the market, their place was to a certain
extent taken by railway stock repair works of Bydgoszcz (PESA), Nowy Sącz (Newag)
and Gliwice. While initially output of the former two included mainly diesel
railcars, built in small numbers for local operators, and later EMUs for
suburban traffic, Electric Locomotives Repair Works (Zakłady Naprawcze Lokomotyw Elektrycznych – ZNLE)
of Gliwice, who were the last to enter the market, finally delivered the
first brand-new Polish electric locomotive in over twenty years – in fact
since the last EM10 from Pafawag was outshopped in 1990. Based
on experience gained with earlier modernizations of electric locomotives
(including ET21, ET22 and EL2) and bearing factory designation E6ACT, this
locomotive has been basically designed for Polish operators, although
two-system variant is also offered. It is suited mainly for heavy freight
traffic, being capable of hauling a 4000-tonne draft at 105 km/h or at 30
km/h at a 6‰ gradient. E6ACT is a thoroughly modern design and employs
state-of the-art control and on-board diagnostic systems. Crew compartment equipment
includes refrigerator and microwave oven. Due to the Co’Co’
axle arrangement, axle load is moderate, only slightly exceeding 19 T. First
prototype, bearing the commercial name ‘Dragon’, was completed in 2009 and
exhibited at the Trako 2009 Fair in Gdańsk,
attracting much attention. During next two years it underwent service tests
with STK (leased to Lotos Kolej), remaining the manufacturer’s property. During
the next Trako Fair in October 2011, a contract was
signed for four examples, ordered by STK; it was completed in April
2014. In August 2016 these locomotives were sold to Industrial Division company, which leased them to various
operators. Currently (September 2020) they are operated by ČD Cargo Poland, Polish subsidiary of
Czech national operator. In September 2012 another order for five examples
followed, this time from Lotos Kolej. First example was outshopped
in February 2014 and the entire order was completed until next May. In
January 2015 Freightliner PL placed
an order for five examples. These locomotives are fitted with auxiliary 735 hp diesel engine and were initially designated E6DCF-DP
(‘DP’ stood for ‘dual power’). First example began tests at the railway
experimental establishment in Żmigród in February
2016 and was delivered to Freightliner
PL in June as E6ACTd-101. It was named ‘Ernest Malinowski’, in honor of a
renowned Polish railway engineer, who was responsible for the design of Ferrocarril Central Andino
in Peru. The entire order was completed until July 2016. A single example,
E6ACTd-106, was ordered for Budokrusz (a large supplier of building materials) and
delivered in March 2017; formally it is owned by Newag. In
all, fifteen examples of E6ACT and E6ACTd were delivered for various
operators before production switched to E6ACTa and E6ACTad, known as ‘Dragon
2’ or ‘Dragon II’. This version was displayed at the InnoTrans fair in Berlin in September 2018. Externally it differs
from its predecessor mainly in headlights, but principal difference is its
full compliance with Technical
Specifications for Interoperability (TSI)
of the European Railway Agency. In
December 2018 three more examples were delivered to STK, followed by two for CTL
Logistics in January 2019; further deliveries, usually of single
examples, followed to several private operators. Most of these locomotives
are formally owned by Newag.
‘Dragon 2’ is certainly well suited to replace obsolescent twin electric
locomotives (classes ET40, ET41 and ET42) in the PKP Cargo fleet,
offering even higher power and tractive effort. Information on the version
for state railways was initially scarce and unofficial. First order, for
three examples designated ET25, was completed in October 2018. Version with
auxiliary diesel engine (E6ACTad) is designated ET26. In September 2019 PKP Cargo ordered 31 locomotives of
this type, including seven fitted with an auxiliary diesel engine and 24
two-system ones, later designated ET43. They were to be delivered until 2022.
A few days later Rail Capital Partners
leasing company ordered five examples. At the time of writing (November 2023) 69 locomotives of this type
were in use. Moreover, an order had been placed by French Akiem locomotive leasing
company for thirty examples, with an option for further fifty. Further orders
are likely to follow. In September 2008 Newag
became the principal shareholder of ZNLE Gliwice, the company finally
changing its name to Newag Gliwice on
February 20, 2013. Production of ‘Dragons’ was transferred to Nowy Sącz in 2016.
Plans for future are quite ambitious. Current ‘Dragon’ offer, apart from the
basic 3 kV DC variant, includes also AC (13 kV 16 2/3 Hz and 25 kV 50 Hz) and
MS (multi-system) versions, as well as a diesel-powered derivative with and
unspecified prime mover of about 3000 hp. The ‘Dragon’ family was later
supplemented by lighter E4 ‘Griffin’ family – completely new design of a
universal Bo’Bo’ multi-system locomotive for
passenger (200 km/h) and freight traffic. Prototype was exhibited at the InnoTrans
fair in Berlin in October 2012. This type is described under a separate
entry. Main
technical data
1)
Until November 2023. 2)
ABB
AMXL450 traction motors in later production examples (one-hour rating
increased by 64 kW). 3)
119 000 kg for E6ACTd. References and
acknowledgments
-
ZNLE Gliwice and Newag folders; -
SK, various issues; -
www.kolejowaklatka.org (website
by Marek Dąbrowski); -
www.ilostan.forumkolejowe.pl. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||