Tr3
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
KPEV Cöln
5901 (Henschel 16443/1919), location and
date unknown. Re-numbered 56 101, this locomotive remained with DR until
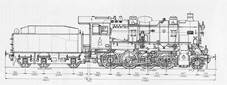
withdrawal in June 1967. Source: Lokomotiv-Archiv Preußen Band 2 (see References). Side drawing
of class G83, © Lokomotiv-Revue (TB
vol. 1). An unidentified KPEV
G83 locomotive (from Henschel?),
location and date unknown. Source: Die Lokomotive July 1926. DR
56 106 (ex Breslau 5381), Henschel
16448/1919, photographed between Klingenberg and Columitz in 1951. This locomotive was withdrawn in 1967
and scrapped in 1970. Photo from my collection. DRG
56 127 (ex KPEV Kassel
5342, Henschel
17129/1920), location unknown, May 9, 1930. Taken over by DR, it was written off in June 1967. Source: www.commons.wikimedia.org.
|
The
most powerful freight locomotive designed and built for Königlich Preußische Eisenbahnverwaltung
(Prussian state railways, KPEV),
was three-cylinder Decapod G12.
This type remained in production between 1917 and 1921, 1509 examples being
delivered by eight manufacturers. After the war a ‘scaled-down’ variant was
proposed by Henschel,
with shortened boiler and 1-4-0 axle arrangement. The idea was to develop a
modern replacement for older medium freighters, many of which had to be
handed over to foreign railway managements as a part of war reparations. Such
locomotive finally emerged as class G83, with prototype (s/n
16443) being outshopped in 1919. Although
the design was basically successful, the very idea of producing a
three-cylinder medium freighter was not particularly favored by KPEV, who tended to value simplicity
of manufacturing and maintenance. It was soon found that cheaper and less
complex two-cylinder locomotives could do the same job. Such engine, classed
G82, was also developed from G12 and remained in production until
1930, with almost 1,000 examples built. Production run of class G83
was much shorter, only 85 engines being built between 1919 and 1920, all by Henschel. Later
they were classed 561. After WWII most of them (62) went to
Eastern Germany, remaining there in use until late 1960s. Four remained with DB, but between 1946 and 1948 were
sold to Osthannoversche Eisenbahnen
and immediately rebuilt into a two-cylinder variant; the last one was
withdrawn in 1964. One example became Soviet war booty and the fate of two is
unknown. PKP took over sixteen
examples, classed Tr3. These complex locomotives found little favor with
Polish railwaymen and their service was
comparatively short: the last one, Tr3-16 (ex 56 181, Henschel
17183/1920) was written off in June 1955. Five were handed over to industry.
Not a single example of this locomotive has been preserved. Main technical data
List of vehicles can be found here. References
and acknowledgments
-
www.beitraege.lokomotive.de/datenbank
(databank by Ingo Hütter); -
Lokomotiv-Archiv Preußen Band 2
by Andreas Wagner (Bechtermünz Verlag,
1996); -
TB
vol. 1; -
Lokomotiven der alten deutschen Staats- und Privatbahnen by Hermann Maey and Erherd Born (Transpress,
1983). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||